Public Domain
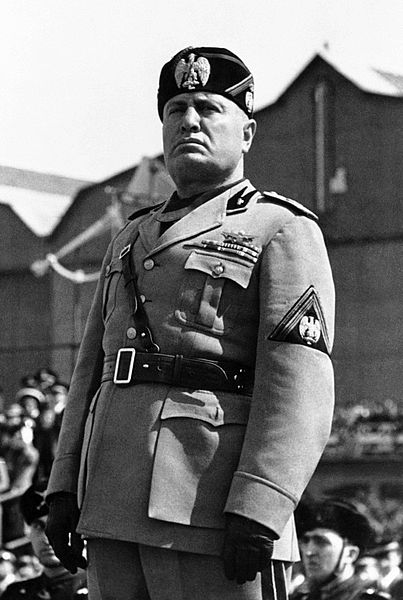
On 25 Jul 1943 the Fascist Grand Council formally voted Mussolini from power and was arrested later after meeting with King Victor Emmanuel III. So, what happened to the once all-powerful Duce? Let’s find out.
Italy had entered into the Pact of Steel with Germany in 1939 which committed Italy to fighting along with Germany if it declared war or was attacked. Mussolini entered the agreement knowing full well Italy did not have the resources or industrial capability for a sustained military conflict. Mussolini had grand ambitions about expanding the Italian sphere of influence in the region and even into central Europe. Mussolini believed that Fascism was on the march and aligning with Hitler seemed a good choice at the time. Italy had successfully invaded Ethiopia (1935-1937) though not without them putting up a strong fight. Using mustard gas against troops and civilians had gotten Mussolini severely criticized and international sanctions.
The war in Ethiopia and his intervention on the side of Franco in the Spanish Civil War had brought Italy closer to Germany with a treaty of mutual interest in 1936. And he needed coal from Germany since international sanctions over Ethiopia had made acquiring it more difficult. Mussolini believed a German-Rome Axis would be how Europe would turn but relying on Germany to supply items like coal meant Italy was more dependent on Germany rather than a true partnership. Mussolini tried to get all kinds of concessions from the British and French after the Munich Agreement in 1938; none were given. He made it clear in speeches (and those by others) that they wanted territory in France, Tunisia, a small part of Switzerland, and Albania. He upped his demands to demand free access to the world’s oceans by breaking British control of key places such as Gibraltar.
From the viewpoint in London, Paris, and elsewhere, his bellicose talk signaled major territorial ambitions. The Fascists mostly supported this though some, like his foreign minister Count Galeazzo Ciano, were concerned about aligning with Germany. Taking on both Britain and France became accepted since they were the major colonial powers that Italy saw as blocking them from achieving their rightful position in the world. On 7 April 1938, Italy invaded Albania and took control in three days. The formal military alliance with Germany (the Pact of Steel) was signed on 2 May 1939 cementing further the military ambitions of both countries together. The Italians thought war with Britain and France would not occur for years but dreadfully miscalculated Hitler’s ambitions.
Italy was not ready for major war operations until 1942 according to his own advisors. The Pact of Steel had said neither side was to enter war until 1943. Italy desperately needed this time in order to get its industry running and lacked critical military industrial production. Both Britain and France had highly developed military industrial production, but Italy was woefully behind in key areas such as automobile production (key to making tanks and other mobile artillery). Additionally, Italy needed to acquire all the needed raw resources needed for war production. Italy was primarily an agriculturally based economy with small pockets of industrial sectors. They needed to setup a supply chain to bring in all the raw materials like coal and import steel. Italy’s merchant marine was not managed in preparation for war and would lose those ships as they were in foreign ports when war was declared by Italy in 1940.
Prior to that, raw materials being sent from European ports to Italy were subject to seizure. Coal, for instance, was shipped out of Rotterdam. The British declared it contraband and seized it, infuriating Mussolini. The Germans offered to ship by train over the Alps while the British countered saying they would supply all of his country’s needs if Italy supplied them armaments. The British hoped to lure Italy away from its alliance with Germany. And it appeared to work as Mussolini had approved a draft contract to provide military equipment. It was suddenly scrapped under intense pressure from Germany caused Mussolini to fold. This decision would come back to haunt him much later down the road.
Italian debt, already large when Mussolini, came to power, had increased thanks to his generous support of General Franco in Spain that increased it. The blockade of coal was strengthened and deeper reliance on German imports of raw materials occurred. The economy was bolstered by the important of goods from Germany, but inflation was occurring causing basic goods and service to become more expensive. When Italy entered the war in 1940, its merchant marine in foreign ports were seized leaving the country without hardly any means of getting needed supplies by cargo vessels.
Adding more to the woes, the warnings of his advisors were accurate. Italy’s army was huge making it a major land force on paper but in reality, lacked modern transport and weapons. The army, because of the weak economy, did not have the needed armaments or supplies for war, and was the major reason it failed. Lightly armored infantry is no match for a fully equipped company of troops with full battle-ready equipment like the British had. Along with both a navy and air force that did not work together well, Italy was ill-prepared for general warfare except for a country that had a worse military than it had. There was poor leadership as well at the top that never had clearly defined military objectives and seemed to go at the whim of whatever Duce wanted them to do. They easily took the lower portions of Vichy France and Corsica. About the only good thing they did in taking that was providing a refuge for fleeing Jews. The Italians did not follow the German lead much regarding the Jews, which caused the Germans frustration over the Italian non-compliance in this area.
The succeeding campaigns in North Africa and Greece ended badly. In North Africa the British put up a good fight and had routed the Italians. Then the Germans arrived with Rommel in charge making it a much tougher campaign for the British and later the Americans; Greece was a total debacle. They invaded from Albania, but the Greeks pushed them back into Albania ending up in a stalemate that cost both sides. Once again, the Germans invaded (the British were using Greece to fly bombing raids into Romania) and successfully took Greece and Crete. Only Yugoslavia was a success but that was because the Germans were part of the campaign and once the country was divided up, Italy got the coastal area.
By 1943 though, things had gotten worse for most Italians. Food and other items were rationed, wartime inflation made everything more expensive, and the war itself was unpopular with most Italians. Mussolini was no longer seen as the great leader and the recent bombing of Rome showed how his boasts were hollow. The invasion of Sicily and later the south by Allied forces showed the proverbial “writing was on the wall.” Mussolini knew that his military could not successfully fight the Allies but stuck to the war because he saw no other option but to fight it out. The Fascist Grand Council knew the war was lost and that Mussolini had lost his stature with the people.
On the night of 24 July and in the early morning of 25 July, the Grand Council met with Mussolini. Accounts of the meeting indicate he was sick, tired, and felt the burden of the military reverses suffered by the Italian military. To some, it seemed he was looking for a way out and it was given to him. The Grand Council voted to remove him from power and transfer some of his duties to the King. While some opposed it, the vote was carried by the majority. Even his son-in-law Count Galeazzo Ciano voted for his ouster. Mussolini seemed dazed by the vote and while his supporters tried to get him to act, he seemed unable to do anything. He would go to his meeting with the King (unshaven and groggy) where he would be arrested. The King told him that General Pietro Badoglio would be taking over as Prime Minister and that the war was lost. He and his family were assured of their safety, and he was whisked away. Mussolini accepted his fall as it absolved him of any more responsibility for the war.
When it was declared Mussolini was out, the general response was one of relief. His fellow Fascists did not stage marches or protests over his dismissal and did nothing to release him from his incarceration on La Maddalena (he would be moved elsewhere). Hitler was furious and knew that the Italians would seek an armistice with the Allies (which was true but in public said otherwise to keep the Germans at bay). For the Allies his dismissal was good news as they hoped it might bring an end to the Italian campaign. And many Italians thought it would as well, Unfortunately the Germans had other plans and that would drag out the war in Italy until June 1944, but that is a story for another time.
Sources:
Foot, J., & Hibbert, C. (2024, July 8). Benito Mussolini | Biography, Definition, Facts, rise, & Death. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Benito-Mussolini
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2009, March 18). Pact of Steel | Italy–Germany [1939]. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/event/Pact-of-Steel
Mullen, M. (2020b, July 23). Benito Mussolini falls from power. HISTORY. https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/mussolini-falls-from-power
Italy between 1922-1945 – The Rule of Mussolini. (n.d.). Life in Italy. Retrieved July 23, 2024, from https://lifeinitaly.com/italy-between-1922-1945-the-rule-of-mussolini/
Warfare History Network. (2023, November 29). Mussolini’s Fall from Power – Warfare History Network. https://warfarehistorynetwork.com/article/mussolinis-fall-from-power/
Axis Alliance in World War II. (n.d.). https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/content/en/article/axis-powers-in-world-war-ii
Wikipedia contributors. (2024d, July 23). Military history of Italy during World War II. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Military_history_of_Italy_during_World_War_II
Suggested Reading
Bosworth, R. J. B. (2006). Mussolini’s Italy: Life Under the Dictatorship, 1915-1945. Penguin Press HC.
Haynes, D. (2023). A brief history of Italy: Tracing the Renaissance, Unification, and the Lively Evolution of Art and Culture.
Hearder, H., & Morris, J. (2001). Italy: A Short History. Cambridge University Press.
Hibbert, C. (2008). Mussolini: The Rise and Fall of Il Duce. St. Martin’s Griffin.
Kertzer, D. I. (2015). The Pope and Mussolini: The Secret History of Pius XI and the Rise of Fascism in Europe. Random House Trade Paperbacks.
Moseley, R. (1999). Mussolini’s shadow: The Double Life of Count Galeazzo Ciano. Yale University Press.
Titanic News Channel is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com.