National Library of France
Public Domain via Wikimedia Commons
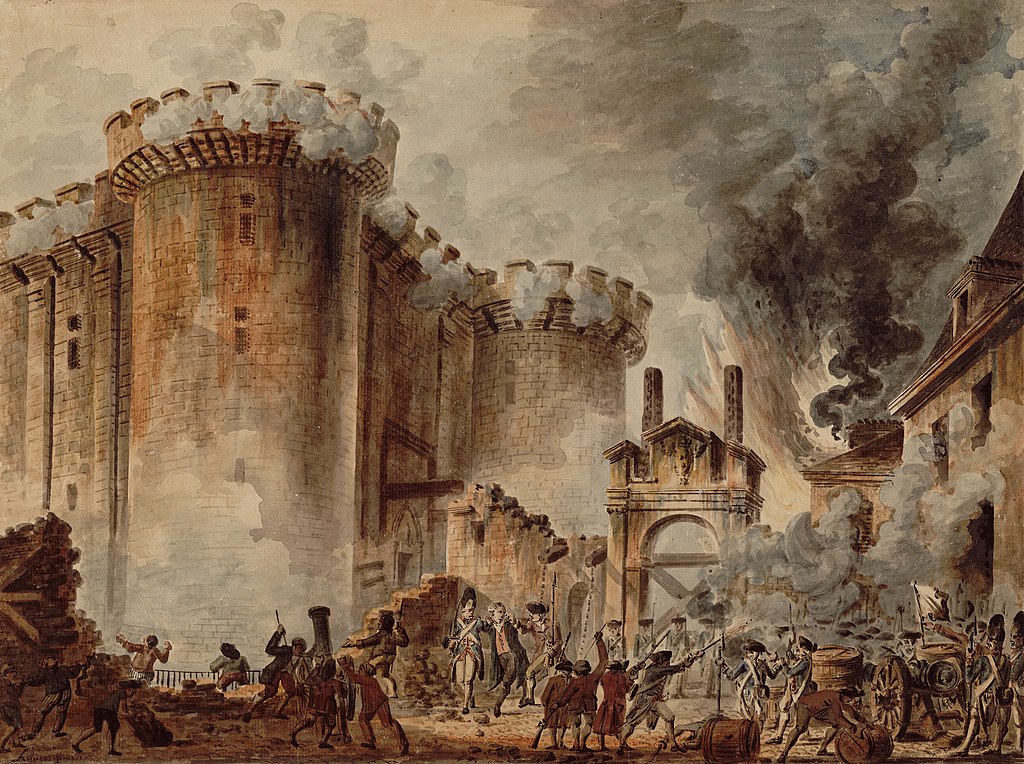
On 14 July 1789, the storming of the Bastille, a formidable stone prison originally built to protect the eastern entrance to Paris, is considered the launch of the French Revolution and celebrated as a holiday in France. The prison often held political prisoners and was seen as a sign of tyranny. By this time in 1789, the prison only held seven prisoners none of whom were of a political nature. Four were charged with forgery and two were considered mad or lunatics. The Bastille was actually being scheduled for demolition to make way for public square.
France was facing economic and social problems. Louis XVI had inherited considerable debt from his predecessor but continued to spend (along with his wife Marie Antoinette) considerable sums of money further deepening government debt. Crop failures in 1788 led to a national famine and the cost bread prices to soar. Unemployment was a factor as well and many thought they had lost jobs due to lessening of customs duties with England (resulting in more jobs there than in France). With violent food riots breaking out, King Louis XVI tried to resolve it through the Estates-General (a national assembly of clergy, nobility and the common person).
While in theory all three were equal, two of the other parts could outvote the third. This left many deputies upset demanding a greater voice and proclaiming their own National Assembly. This would lead to the famous Tennis Court Oath of 20 June 1789 not to separate until they had a constitution. Many nobles and clergy crossed over to this National Assembly which Louis XVI gave consent to. His ordering of army regiments into Paris though made many fear he was going to break up the assembly by force. The dismissal of Jacques Necker, a non-noble minister for the government on 11 July, triggered massive protests and destruction of custom posts. Custom posts were hated as they imposed taxes on goods.
On 14 July a mob seized muskets and cannons from a military hospital and then decided to get more at the Bastille. The governor of the Bastille saw the mob and invited them in to discuss terms of surrender. Outside the crowd grew restless awaiting word and it is possible some thought the delegates had been arrested. A group climbed over the outer wall and climbed in to open the drawbridge to the courtyard. The governor broke his pledge not to fire and bullets rang out killing 100 outright leaving others wounded. The royals only lost one soldier. The arrival of the French Guards, sympathetic to the mob, would force the governor to surrender after having cannons blasting away at the Bastille. Without adequate provisions, he surrendered the Bastille. Some of the royalist troops would be butchered after the surrender. The governor was taken prisoner and beheaded by the mob.
Aftermath
The Bastille was dismantled, and its only prisoner later would be Louis XVI. He would be executed on 21 January 1793 along with his wife. The French Revolution, once thought a means to reform France into a constitutional monarchy, slid into a revolutionary government that completely overturned the ancien regime. During its tenure, it became increasingly bloody killing off enemies of the new order. Anyone who was thought to disagree with them could be denounced and executed. Instead of creating a better stable system, it became one long food riot as one professor said to me once. And the revolutionaries fought amongst themselves as to who was the better one to lead. That led to more bloody executions and the guillotine became the image of the French Revolution. Ultimately the people tired of this turmoil and wanted order. And it would come from Napoleon Bonaparte, but that is another story.
Sources
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2024c, July 11). Bastille Day | Definition, history, traditions, celebrations, & facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/Bastille-Day
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2024a, May 17). French Revolution | History, Summary, timeline, causes, & facts. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/event/French-Revolution
Mullen, M. (2023, July 14). Bastille Day – Definition, Date & facts | HISTORY. HISTORY. https://www.history.com/topics/european-history/bastille-day
Suggested Reading
Clarke, S. (2019). The French Revolution and What Went Wrong. Arrow.
Davidson, I. (2018). The French Revolution. Pegasus Books.
Dickens, C. (1998). A Tale of Two Cities. Courier Corporation.
Doyle, W. (2018). The Oxford History of the French Revolution. Oxford University Press.
De Tocqueville, A. (2020). The State of Society in France Before the Revolution of 1789: And the Causes Which Led to That Event (H. Reeve, Trans.). Independently Published.
Palmer, R. R. (2017). Twelve Who ruled: The Year of Terror in the French Revolution. Princeton University Press.
Titanic News Channel is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com.