German Federal Archives
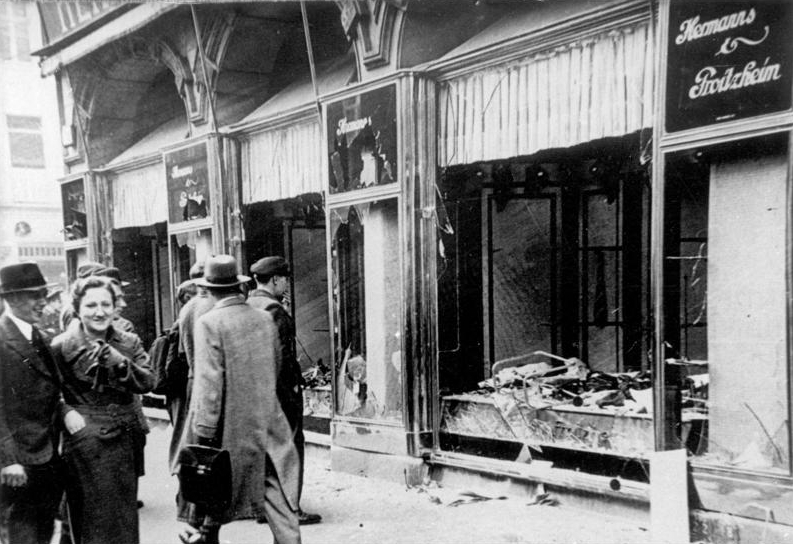
On November 9-10 1938, a violent wave of anti-Jewish pograms broke out in Germany, Austria and Sudetanland. Called Kristallnacht (means literally Night of Crystal but commonly called Night of Broken Glass) violent mobs destroyed synagogues, looted Jewish owned businesses, homes and schools, and arrested 30,000 Jewish men who were sent to concentration camps. Police and fire were ordered to stand down and only act to prevent damage to German buildings. Nearly all the Jewish synagogues were torched, except those close to historical sites or buildings.
Thanks to the presence of foreign reporters in Germany at the time, this event became known to the world changing perceptions about the Nazi regime.
Nazi officials depicted the event as a genuine response of the people to the assassination of German diplomat Ernst vom Rath in Paris by Herschel Grynszpan on 7 Nov 1938. Grynszpan, a 17-year old boy, was distraught over his family’s deportation from Germany to Poland. Vom Rath’s death two days later coincided with the anniversary of the 1923 Beer Hall Putsch. The Nazi Party leadership assembled in Munich used the occasion to push for demonstrations against the Jews arguing that “World Jewry” had conspired to commit the assassination. However, Hitler ordered that the demonstrations should not look they were prepared or organized by the Nazis’. They had to look spontaneous. Propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels was the chief instigator following Hitler’s orders in his speech to the assembled party officials.
The regional Nazi party leaders issued instructions to their local offices about how to proceed. Reinhard Heydrich, as head of the Security Police, sent instructions to headquarters and stations of the State Police and SA leaders about the upcoming riots. The SA, Hitler Youth and others were ordered to wear civilian clothes so it would like genuine public reaction. Heydrich ordered the rioters to not endanger non-Jewish German life or property. The rioters were also ordered to remove all synagogue archives prior to vandalizing and destroying them. Police were ordered to arrest as many young Jewish men their jails would hold.
Violence began to erupt in the late evening of 9 November and in the early morning hours of 10 November. The two largest Jewish communities, Berlin and Vienna, would see massive destruction. Mobs of SA and Hitler Youth shattered store windows. They attacked Jews in their homes and looted. They publicly humiliated Jews in the streets. Many Jews were killed as well though numbers vary but likely in the hundreds. Jewish cemeteries were desecrated. Those who were arrested by the SS and Gestapo ended up in Buchenwald, Dachau and Sachsenhausen and other camps as well. Many would die in the camps and many who were released had promised to leave Germany. Kristallnacht would spur Jews to emigrate from Germany.
Aftermath
German leaders blamed Jews for the riots and fined the Jewish community one billion Reich Marks. To pay the fine, Germany seized property and insurance money. This left Jewish owners personally responsible for repair costs. Kristallnacht accelerated more laws and decrees to deprive Jews of the property and their ability to make a living. The Aryanization of businesses required many Jewish owned businesses and property to be transferred to non-Jews. Usually they got paid a fraction of the true value of the business or property. By this time, Jews could not be government workers or in any aspect of the public sector. Now many professions in the private sector were unavailable as well (doctors, lawyers, accountants etc.). Jews were no longer allowed to have a driver’s license, expelled from any German school they were still attending, be admitted to German theaters (movies and stage) or concert halls.
Kristallnacht was covered by newspapers in the United State and elsewhere. It was front page news in the United States in large banner headlines and perhaps the largest story of Jewish persecution to be reported during the Nazi years. Despite attempts by German censors to prevent images from getting to newspapers in the United States, pictures got out and got printed in the 28 November 1938 issue of Life magazine. A telling heading published on the front page of the Los Angeles Examiner says it all:
Nazis Warn World Jews Will Be Wiped Out Unless Evacuated By Democracies (23 Nov 1938)
President Roosevelt denounced the attack on Jews at a press conference on 15 November 1938 and recalled the US ambassador to Germany (the US was the only one to do this) and not replaced till 1945. A chargé d’affaires would handle diplomatic relations with Germany until war was declared in 1941. The US and other countries had restrictive immigration quotas in place at the time. However, 12,000 German Jews already in the United States were allowed to stay and not be sent back to Germany. Attempts to allow refuge for children under 14 were introduced in Congress but despite widespread support did not get voted into law.
Kristallnacht is rightly seen as the turning point in Nazi policy and world-wide opinion of the regime. The Nazi’s began concentrating their pogroms into the hands of the SS and more restrictive policies on the Jews. They radicalized and expanded the measures to remove Jews from the economic and social life of Germany. It would lead to policies of forced emigration and deportations to the East and the goal of Judenrein-a Germany free of Jews.
Sources
———. “Nazis Launch Kristallnacht.” HISTORY, November 7, 2022. https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/nazis-launch-kristallnacht.
Berenbaum, Michael. “Kristallnacht | Definition, Date, Facts, & Significance.” Encyclopedia Britannica. Last modified November 2, 2024. https://www.britannica.com/event/Kristallnacht.
“Kristallnacht.” https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/content/en/article/kristallnacht..
Suggested Reading
Gilbert, Martin. Kristallnacht: Prelude to Destruction. Harper Collins, 2006.
Karlauf, Thomas, and Uta Gerhardt. The Night of Broken Glass: Eyewitness Accounts of Kristallnacht. Polity, 2021.
Titanic News Channel is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com.