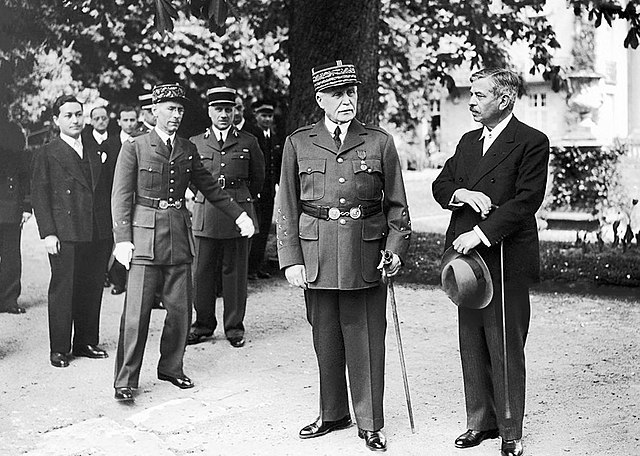
Pierre Laval

Public Doman via Wikimedia Commons
After the German invasion of France in 1940, the Vichy state was created with Henri Pétain in charge and Pierre Laval as head of state. Laval had originally begun his political life as a pacifist but during the 1930’s shifted more towards supporting Fascism. In 1935 he sought France to align with Italy rather than make a deal with the Soviet Union (he had become anti-communist by then). By 1939 he was against war with Germany and encouraged the antiwar faction to keep the government from using troops against Germany when it invaded Poland in September 1939. After the German invasion in 1940, he helped push for an armistice and got himself into the new Vichy government.
Pétain did not care much for him and dismissed him in 1940 after he found he was negotiating with Germany on his own. He had developed a friendship with Hitler and thus by 1942 had become the real ruler of Vichy while Pétain remained as a figurehead. During the time he ran the regime, he actively collaborated with Germany in carrying out their deportation of Jews and enforcing oppressive laws on French citizens. Laval had to flee to Germany when France was liberated in August 1944. He escaped to Spain when Germany was defeated in 1945, but Franco had him expelled. He tried hiding out in Austria but ultimately surrendered to American forces. He was then sent back to France to stand trial for his actions during the German occupation. The trial was quite sensational and revealed his complicity in working with the Germans. He was convicted of treason and sentenced to death. He tried taking his own life, but he was nursed back to health so he could be executed by firing squad on 15 October 1945. Petain, revered for his leadership in World War I, was tried and found guilty of treason. He was also to be executed but French president Charles de Gaulle changed it to life imprisonment. He was sent to the island of Yeu and died there in 1951.
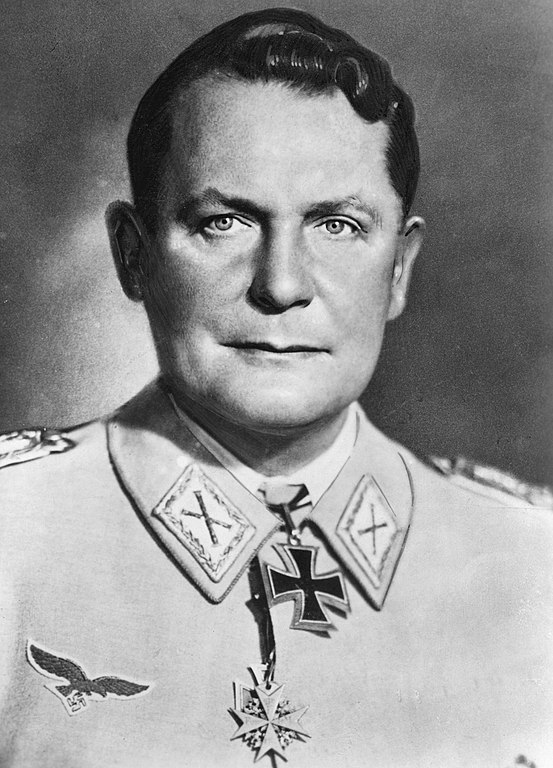
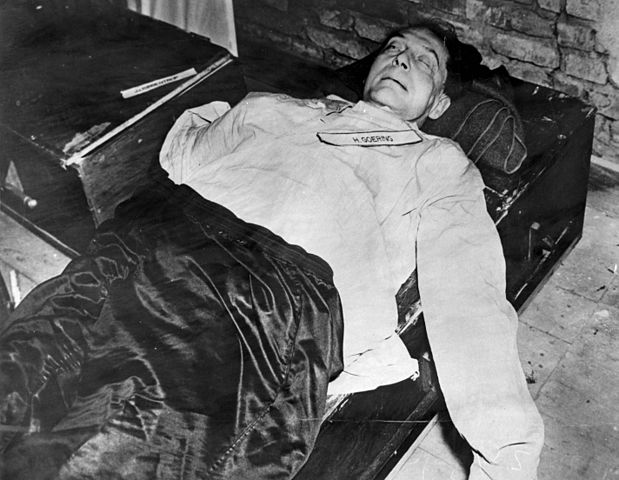
Hermann Goering (15 October 1946)

Public Domain via Wikipedia
Hermann Goering once was not only the head of the Luftwaffe (German Air Force) but at one time Hitler’s designated successor. As Reichsmarschall, he held the highest military rank and answered only to Hitler. He had other titles as well (president of the Reichstag, prime minister of Prussia, chief liquidator of sequestered estates and much more). He established concentration camps to imprison enemies and was instrumental in many anti-Jewish policies such as Kristallnacht and confiscation of Jewish money and property. Known for his flamboyant outfits that showed off his decorations and his displays of stolen artwork, his only threat was from Heinrich Himmler head of the SS.
His stature began to fall when the Luftwaffe failed to deliver in the Battle of Britain, and failing to deter Allied bombings of Germany. Other German officers had a low opinion of his military strategies leading him to become depressed and more addicted to painkillers. By the end of the war, Hitler had turned away from his old comrade and dismissed him when he learned he was negotiating with the Allies. He was captured at the end of the war and was tried in Nuremburg for various crimes against humanity.
He was convicted and sentenced to be hanged. Before that could be carried out, he took a potassium cyanide capsule and died. Speculation on how he obtained the capsule is either he had managed to hide it successfully when he was initially captured, or it had been secretly delivered to him. Cyanide capsules were found on his person when he was captured. Some speculate that US Army lieutenant Jack G. Wheelis had retrieved a capsule after Goering gave him some personal effects, but it has never been substantiated. Former US Army private Herbert Lee Stivers claimed in 1945 that it was likely hidden in a fountain pen a German woman asked him to smuggle into the prison. Goering’s body was later cremated, and ashes thrown into the Isar River.
Public Domain
Sources:
Pierre Laval
———. “Pierre Laval | French Prime Minister, Collaborator & Statesman.” Encyclopedia Britannica. Last modified October 11, 2024. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Pierre-Laval.
Reed, Betsy. “The Execution of Pierre Laval.” The Guardian, October 16, 2008. https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2008/oct/16/fromthearchives.
———. “Vichy Leader Executed for Treason.” HISTORY, October 14, 2020. https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/vichy-leader-executed-for-treason.
Hermann Goering
Fraenkel, Heinrich, and Roger Manvell. “Hermann Goring | Biography, History, Death, & Facts.” Encyclopedia Britannica. Last modified October 11, 2024. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Hermann-Goring.
Deutsche Welle.“Secret Lifted Around Göring’s Suicide,” Dw.Com, February 9, 2005, https://www.dw.com/en/secret-lifted-around-g%C3%B6rings-suicide/a-1482751.
———. “High-ranking Nazi Leader Hermann Göring Dies.” HISTORY, October 14, 2020. https://www.history.com/this-day-in-history/hermann-goering-dies.
“Hermann Göring.” https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/content/en/article/hermann-goering.
Titanic News Channel is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com.



