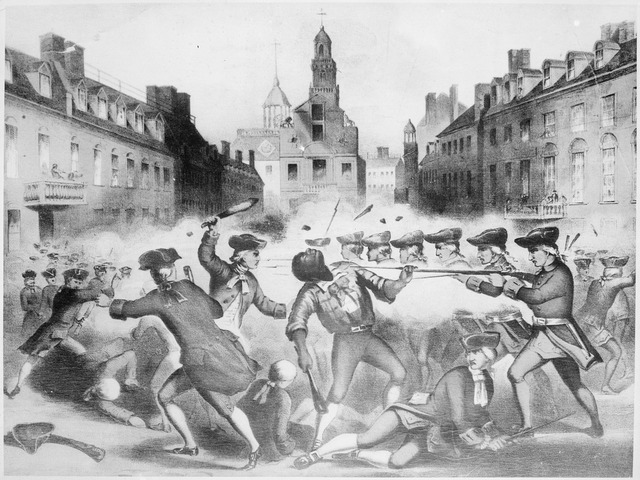
Public Domain/U.S. National Archives and Records Administration (via Wikipedia)
It was a cold snowy night on 5 March 1770 when a mob of American colonists gathered at the Customs House in Boston. The protestors were objecting to the occupation of Boston by British troops. The troops had been sent in 1768 after resentment grew at unpopular taxation measures (Stamp Act and Townshend Act) passed by the British parliament. Since no one from the colonies was represented in parliament, it led to a backlash back in Boston.
Tensions had been running high for a while. Skirmishes between soldiers and colonists, and between patriot colonists and loyalists (colonists loyal to Britain) had been going on for a while. Loyalist stores were vandalized and customers intimidated. One such attack on a loyalist store on 22 Feb 1770 ended tragically. A Customs officer (Ebenezer Richardson ) tried to break up the rock throwing crowd by firing his gun through the window of his home. He ended up killing an 11 year old boy named Christopher Seider. This enraged the Patriots and tensions between Patriots and British soldiers were raised.
The one guard outside the Customs House was facing a mob and called for assistance. The commanding officer of the Customs House, Captain Thomas Preston, ordered his soldiers to fix their bayonets and join the guard outside. The colonists began throwing snowballs, which hit some of the troops. One of the troops, Private Hugh Montgomery, was hit and fired back. Others fired as well. When the smoke cleared, five were dead or dying and three more were injured. The five that were killed were Crispus Attucks (African American), Patrick Carr, Samuel Gray, Samuel Maverick and James Caldwell. Many consider them the first casualties of the American Revolution.
Aftermath
The British soldiers were put on trial and were defended by John Adams and Josiah Quincy. Two soldiers were convicted of manslaughter in December 1770. The two soldiers had their thumbs branded with an M for murder as punishment.The incident would be used by the patriot group Sons of Liberty (formed in 1765) who advertised this as a just cause for removal of British troops.
Paul Revere made an engraving that was widely distributed showing the British soldiers lining up to shoot the patriots. Though not accurate, it helped convey an anti-British message to many in the colonies. Tension decreased for a while but many were unhappy at the lack of representation in British parliament. The hated Stamp Act had already been repealed by this time (in 1766) but the Declaratory Act passed at the same time said parliament had the right to pass any colonial legislation it saw fit. Rather that quell the tension, it was made worse. Patriot colonists were outraged that as citizens of the British colonies they had no voice in government on any of these major issues like taxes or how justice was to be administered. It would lead to growing tension until the revolt would break out in earnest in 1775.
Sources:
Wallenfeldt, Jeff. “Boston Massacre | History, Facts, Site, Deaths, and Trial.” Encyclopedia Britannica, 5 Mar. 2024, www.britannica.com/event/Boston-Massacre.
Onion, Amanda. “Boston Massacre: Causes, Date and Facts | HISTORY.” HISTORY, 11 Aug. 2023, www.history.com/topics/american-revolution/boston-massacre.



