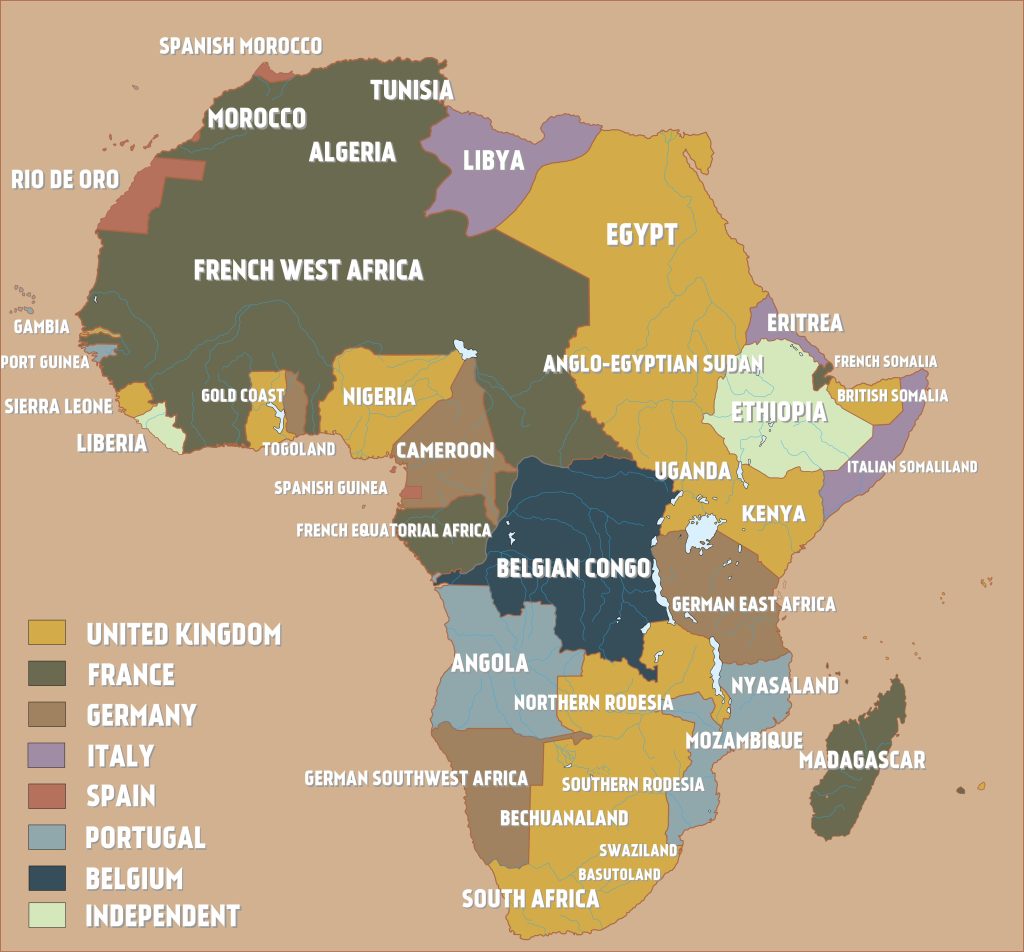
Source:Cobh Heritage Centre, Cobh Ireland/Wikimedia Commons
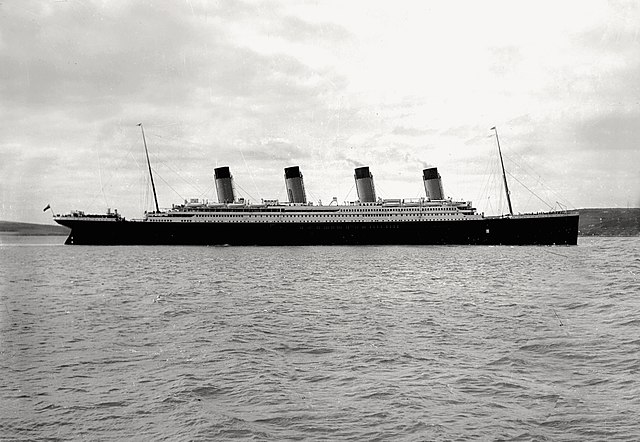
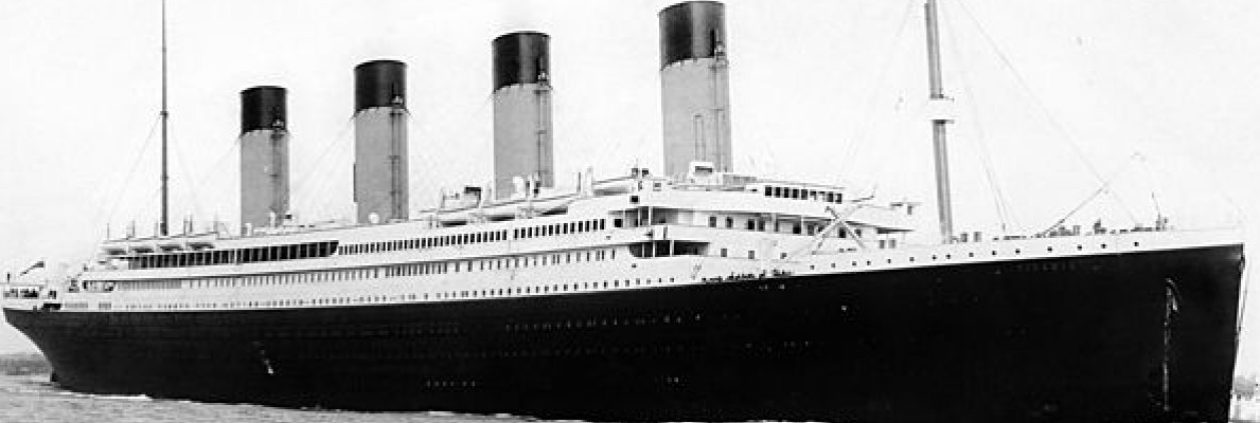
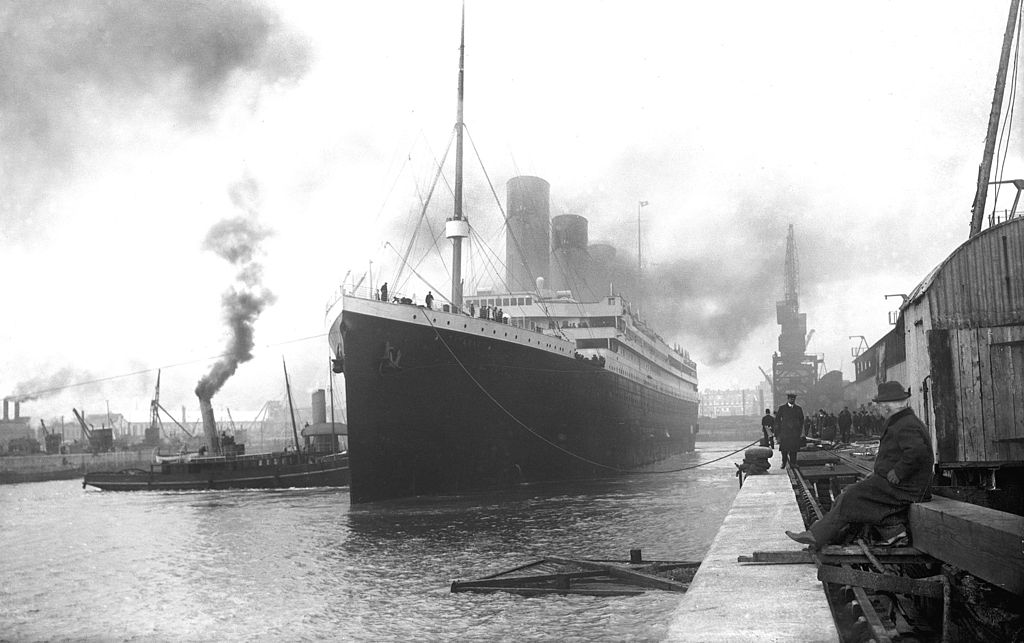
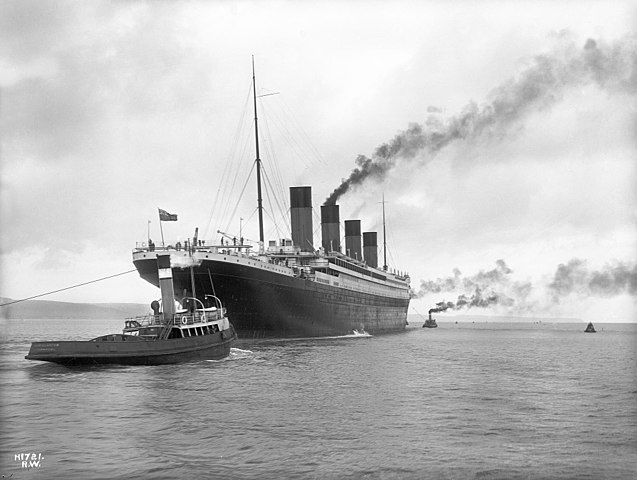
RMS Titanic arrived at 11:30 am at Cork Harbour, which is on the south coast of Ireland. Cork Harbour is a natural harbour and a river estuary at the mouth of the River Lee in County Cork. It is considered one of the larger natural harbours in the world and has been used as a working port for centuries. Near the entrance is Roches Point, where its lighthouse has been guiding ships since 1817 (the original was replaced in 1835 and fully automated in 1995). Queenstown, like Cherbourg, did not have the dock facilities to handle a ship of Titanic’s size.
It was a relatively warm day with a brisk wind (and some clouds in the sky) as Titanic made its last European stop. The tenders America and Ireland were used to bring the 123 passengers aboard: 3 First Class passengers, 7 Second Class passengers, and 113 Third Class. There were seven people who disembarked at Queenstown who had booked passage from Southampton to Queenstown. Among those who disembarked was Francis Brown (later Father Francis Brown, S.J.) who was an avid photographer. His pictures taken aboard Titanic would be the last known photographs taken aboard ship. Kate Odell, another cross-channel passenger who got off in Queenstown, also took some photos as well.
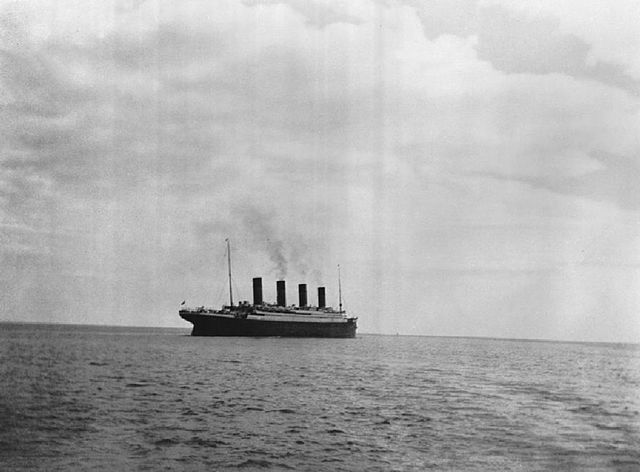
Titanic would weigh anchor at 1:30 pm and begin her journey to New York. A picture of her leaving Queenstown would be the very last ever taken while she was afloat. She would not be photographed again until September 1985 when her wreck was discovered on the bottom of the Atlantic Ocean. Titanic was scheduled to arrive in New York on April 17.

Public Domain
[To be continued with next posting]
Sources
Books
Behe, George TITANIC: SAFETY, SPEED AND SACRIFICE, Transportation Trails, Polo, IL 1997
Eaton John P. & Haas Charles, TITANIC TRIUMPH AND TRAGEDY, SECOND EDITION, W.W. Norton & Company, New York, New York, 1995 First American Edition
Lord, Walter, A NIGHT TO REMEMBER, Holt Rinehart and Winston, New York, New York, 1955. Multiple revisions and reprints, notably Illustrated editions (1976,1977,1978 etc)
Lord, Walter, THE NIGHT LIVES ON, Willian Morrow and Company, New York, New York, 1986 (First Edition)
Lynch, Don & Marshall Ken, TITANIC AN ILLUSTRATED HISTORY, Madison Press Books, Toronto, Ontario Canada, 1992
Internet
Encyclopedia Britannica, www.britannica.com/search?query=Titanic.
“Encyclopedia Titanica.” www.encyclopedia-titanica.org.
“The Titanic: Sinking and Facts | HISTORY.” HISTORY, 12 Mar. 2024, www.history.com/topics/early-20th-century-us/titanic.